GENERAL
How to be a Good Guest
Where is Bat Cave?
The AREA
Area rock Layers
Topography
Geomorphology
Geological History
The Paleozoic
The Mesozoic
The Cenozoic
Water
The Hydrologic Cycle
Solution
Solution chemistry
Karst Landscapes
Erosional Features
Depositional Features
Environmental Issues
BAT CAVE
How was Bat Cave formed?
Surface Plan of the site
Map of the Cave
Life in and around Bat Cave
A Virtual Trip Through Bat Cave
TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE
 GEOLOGIC
HISTORY OF THE AREA
GEOLOGIC
HISTORY OF THE AREA
545-245 MY (=Million Years) Ago
In Geology we now understand that the earth's outer layer, the lithosphere, is made of enormous slabs of rock some 60 miles thick that float on the layer beneath it, the asthenosphere. Those lithospheric slabs called plates, move, collide and separate, carrying their embedded continents with them. So, the history of Florida is also part of the history of plate movement.
The specifics of the earliest history of Florida are lost in the mist of time. The oldest rocks that give us a record of the events of the earliest Earth are buried so deeply that they are just about inaccessible. We do know however that Florida's origin lies with that of the southern continents, more likely Africa. Florida fossils recovered from the Early Paleozoic (Ordovician Period to Devonian Period) rocks of Florida indicate that life here was closely related to life in rocks of the same age in South America, Africa and Eurasia, but NOT those of the US continent. In those days, Florida was part of a supercontinent we call Gondwanaland, that itself was formed by the earlier welding together of the southern continents, and not part of the northern group of continents called Laurasia.
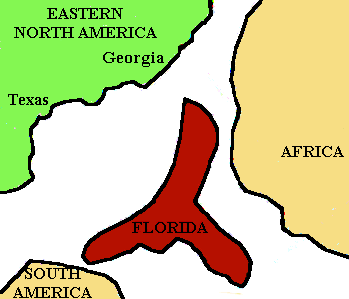
Presumed location of Fla. in Mississipian time. |
During Late Paleozoic time, Gondwanaland joined with Laurasia to form a single landmass that contained all the existing continents called Pangea. In the Pennsylvanian Period, somewhere around 300 MY ago, Florida was welded to the North American continent, certainly a fait accompli by Permian time. | 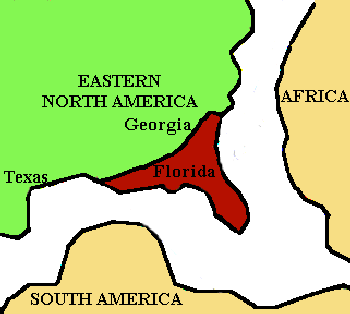
Location of Fla. by Pennsylvanian time. |
245-66.4 MY Ago
245-208 MY Ago
Throughout Triassic time, the Gulf Coastal area, including Florida, is land. In Late Triassic, the supercontinent Pangea begins to crack, break up and rift apart. Great grabens form, places where the lithosphere is foundering as this supercontinent rips apart. Late Triassic rocks mostly consist of sediments washing into those grabens from the bordering continents.
The Jurassic Period
208-144 MY Ago
In Early Jurassic time, the rocks are still terrestrial (deposited
on land), representing continental sediments that are washing in the rift
grabens that is formed as the Florida Platform separates from the African
Plate. The Atlantic Ocean is opening. As North America also separates from
South America, the Gulf of Mexico also begins to form, and sea water begins
to flood the newly forming Gulf. Beginning in the Late Middle Jurassic,
as the growing Gulf is intermittently shut off from oceanic waters, the
waters of the Gulf evaporate, depositing over 3000' of evaporites (mainly
salt). Eventually, by Late Jurassic, as the Gulf continues to open, circulation
is no longer shut off and evaporites are no longer being deposited. Instead,
carbonates (limestones and dolomites) are being put down as the first widespread
ocean encroachment on land begins and continues into Cretaceous time.
The Cretaceous Period
144-66.4 MY Ago
In the Early Cretaceous, as seal level continues to rise, carbonate
accumulation continues along the margin of the Florida platform. In the
early part of the Middle Cretaceous, there is a rapid fall of sea level,
soon followed by a rise, to eventually reach the one of the highest sea
levels of all times. All along the East Coast, including Florida, a carbonate
platform very similar to the Great Barrier Reef develops (except immensely
larger) and limestone deposition and reef formation continue through most
of the Cretaceous. Climates are warm, and in the Gulf of Mexico, warm currents
flow from the Atlantic into the Pacific ocean.
This carbonate deposition ends before the end of the Cretaceous and
there is about a 10 million year gap in the depositional record till deposition
resumes in the Middle Paleocene. So, unfortunately, the Florida record
is silent on the great extinction at the end of the Cretaceous and its
causes.
On to the Cenozoic