based upon? (pp 387-388)
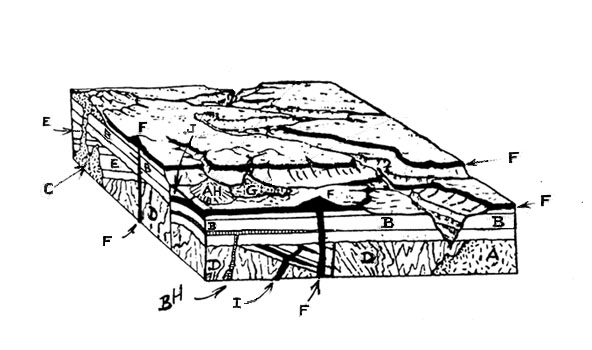
91. List the relative sequence of events as shown in the block diagram below. (pp. 375, 378, 392)
EXAM QUESTIONS TO FOCUS ON WHILE WATCHING THE TAPES, DOING THE READING OR LOOKING AT THE NOTES ON THE NET
ESSAY QUESTIONS FOR EXAM 2
(Includes Tapes 12, 14, 13, 15, 17, 18, 10, and 11)
Tape 12- Minerals
48. Describe the basic layout of any atom using the basic particles, their characteristics and their arrangement in the atom
49. What is an element? (pp 24-25)
50. Describe the geologically important ways in which atoms make bonds (pp 25-28)
51. Define mineral and rock. Explain why "mineral" and "rock" are not
the same term. What characteristics make them
different? Not all rocks are composed
of minerals. Give two examples of rocks that contain no minerals.
Give two examples of rocks that contain
only one mineral (p 23)
52. Explain the difference between classifying minerals chemically (groups)
and identifying them using physical
properties (pp 28-38)
53. List the major elements that combine to form 98% of the materials in the crust (p. 32)
54. Discuss silicates. What is their basic structure? How is this structure
linked to form silicate minerals?
(pp 31-37)
Tape 14 - Intrusive Igneous Rocks
55. Offer three reasons why igneous rocks are called primary rocks (Instructor)
56. What does Bowen’s reaction series tell us about igneous minerals and rocks? (pp. 49-52)
57. Explain how a single magma can give rise to rocks of felsic. intermediate
and mafic composition.
(pp. 44-45, 48-52, 53-58)
58. Name the three basic igneous rock textures and discuss the factors
that determine where and why they occur
(pp. 45-48)
59. Explain the importance of granite and basalt (pp. 53 and 57)
60. How, where and why does magma originate? What are the tectonic processes involved? (pp 85-91)
61. Compare and contrast a sill, dike, laccolith, stock and a
bathohith (pp 82-85)
Tape 13 - Vulcanism
63. Explain the relationship hetween volcanism and plate tectonics. (pp. 85, 87—91)
64. What factors control the viscosity of a lava? (pp. 65-69)
65. Describe, compare and contrast the shape, internal structure and
lava characteristics
(including composition, temperature
and viscosity) of plateau basalts, shield and composite
volcanoes, plug domes and cinder cones.
(pp. 71-81)
66. Compare quiet and explosive eruptions. What are the factors
that cause them to be different?
(pp. 65-71)
67. Explain how volcanic eruptions affect climate and the atmosphere.
(p. 90)
Tape 15 - Weathering and Soils
68. What are the major agents, processes and products of mechanical (physical) weathering? (pp. 95-97)
69. What are the major agents processes and products of chemical weathering? (pp. 97-99)
70. Explain why the minerals formed early in Bowen’s reaction series
are also most susceptible
to weathering. (p. 99)
71. List the major physical components of a soil and explain their role
in supporting plant life.
(pp. 100-102)
72. Discuss the factors that control soil formation (be sure to
focus on the importance of climate).
(pp. 102-104)
73. Describe the development of a soil profile. (pp. 104-106)
74. Describe the main types of soils. (pp. 106-107)
Tape 17 - Sedimentary Rocks
75. Describe how sediment becomes a sedimentary rock. (pp. 114-1 15, 123-124)
76. Explain the basis of the classification of sedimentary rocks. (pp. 115-123,124-126)
77. Name the three most common sedimentary rocks. What are their relative
abundances and why?
(pp. 116-117, 120-122, Instructor)
78. Sedimentary rocks may contain cross beds, graded beds, mudcracks,
ripplemarks and/or fossils.
Describe how these features can be used
to interpret their environments of formation. (pp. 126-130)
79. Describe all he different possible origins of limestones. (pp. 120-122)
80. Define sedimentary rocks and identify what makes them important
to us. (pp. 114-115)
Tape 18 - Metamorphic Rocks
81. Discuss the conditions involved in the mctamorphism of a pre-existing
rock. Discuss the agents and the
actual changes that take place
in the rock (pp. 139-142)
82. Name and briefly describe the principal types of metamorphism?
Where do they occur most commonly?
Relate them to plate tectonics
if possible (p 139. pp 147-151)
83. Describe step by step, how a shale might evolve into a gneiss. (pp 142—144)
84. Diagram the rock cycle to show the relationship between the
three rock types (pp 16-1 8)
Tape 10 - Geologic Time & Tape 11 - Evolution Through Time
85. What is the significance of Hutton’s concept of Uniformitarianism’?
How did it change how we interpret
the Earth’s history ? How has
the concept itself changed over time? (pp 2-6. 371)
86. Describe the difference between absolute and relative time (pp. 372-382)
87. List the methods that arc used to establish a sequence of events in a local sequence (pp 372-382)
88. Explain the significance of fossils to a geologist (at least
4 uses); include the use of fossils in establishing
a relative time scale, and for
correlation (pp 377-382)
89. Explain how radioactive isotopes are used to figure out absolute
time. How are absolute dates used in the
time sequence? (pp 382-387)
90. Explain how the geologic time scale has been constructed.
What are the major eras of the Phanerozoic Eon
based upon? (pp 387-388)
91. List the relative sequence of events as shown in the block diagram
below. (pp. 375, 378, 392)

The relative sequence of events in this block diagram can be determined by using the principles of relative time. Please write the sequence below using the letters for the different Rock Units, starting with the oldest event.
ROCK UNITS
AGE SEQUENCE
A. Igneous (intrusive)
Youngest ____________
B. Sedimentary
____________
C. Igneous (intrusive)
____________
D. Metamorphic
____________
F. Sedimentary
____________
F. Volcanic
____________
G. Sediments
____________
H. Sediments (same age as BH igneous/intrusive)
____________
I. Igneous (intrusive)
____________
J. Sedimentary (the little wedge on top of F, below AH
Oldest ____________